31 March 2024: Review Articles
Differentiation of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Comprehensive Review of Imaging Techniques and Future Applications
Weijian Zhu 12BCEF , Sirui Zhou 3D , Jinming Zhang 1D , Li Li 4B , Pin Liu 2A , Wei Xiong 1A*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943168
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943168
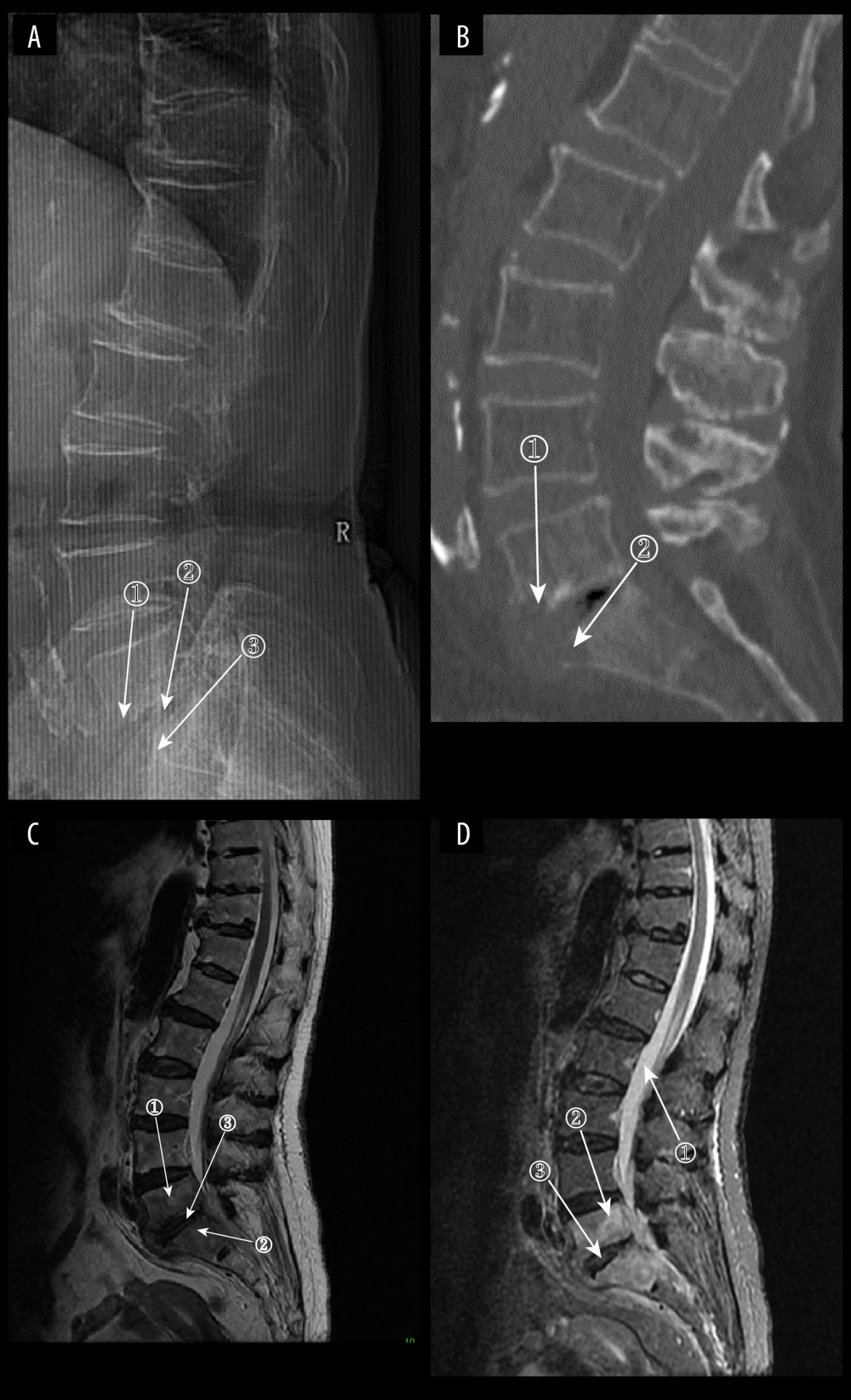
Figure 8 (A) Plain radiograph of early fungal spondylitis (FS). Markers 1 and 3 show localized bone destruction at L5–S1, and marker 2 shows no significant narrowing of the intervertebral space. (A–C) Images of the same patient, who had an interval of approximately 30 days between the onset of symptoms and the time of the radiographs. (B) Plain computed tomography in early FS. Bone destruction is seen in the margins of the L5–S1 vertebrae at markers 1 and. (C) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in early stages of FS. This image is a T2WI sequence. A small intraosseous abscess is shown at marker 1, a striated shadow under the vertebral endplate is shown at marker 2, and an infected disc is shown at marker. (D) MRI in early stages of FS. This image is a short Tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence. Density at marker 1 is 376, marker 2 shows diffuse high signal in the vertebral body with a density of 312, which is lower than the cerebrospinal fluid density value, and marker 3 shows a relatively preserved intervertebral space height (ITK-SNAP. Version 4.0.2. Paul Yushkevich, Jilei Hao, Alison Pouch, Sadhana Ravikumar et al at the Penn Image Computing and Science Laboratory; Adobe Illustrator 2022. 26.5. Adobe Inc.).


